You are looking for information, articles, knowledge about the topic nail salons open on sunday near me how many moons could fit inside the sun on Google, you do not find the information you need! Here are the best content compiled and compiled by the Chewathai27.com team, along with other related topics such as: how many moons could fit inside the sun All the energy of the earth comes from, Talk about the sun, The birth of the Sun, Fact about the Sun, The biggest star, UY Scuti, Nineplanets org Earth
This means the number of Moons required to fill the Sun is 50 times more than the number of Earths required. So, a total of 65 million Moons can fit inside the Sun.It would take around 64.3 million Moons to fit inside the Sun, filling it whole. If we were to fill the Earth with Moons, we would need approximately 50 Moons to do so.Our Sun is a medium-sized star with a radius of about 435,000 miles (700,000 kilometers). Many stars are much larger – but the Sun is far more massive than our home planet: it would take more than 330,000 Earths to match the mass of the Sun, and it would take 1.3 million Earths to fill the Sun’s volume.
Contents
How many Earth moons could fit inside the Sun?
It would take around 64.3 million Moons to fit inside the Sun, filling it whole. If we were to fill the Earth with Moons, we would need approximately 50 Moons to do so.
How many earth can go inside sun?
Our Sun is a medium-sized star with a radius of about 435,000 miles (700,000 kilometers). Many stars are much larger – but the Sun is far more massive than our home planet: it would take more than 330,000 Earths to match the mass of the Sun, and it would take 1.3 million Earths to fill the Sun’s volume.
Are there 200 moons in our solar system?
Earth has one moon, and there are more than 200 moons in our solar system. Most of the major planets – all except Mercury and Venus – have moons. Pluto and some other dwarf planets, as well as many asteroids, also have small moons.
How many moons make a sun?
Complete answer: The Sun, by its definition, is not a planet but a star. Since a star does not have any moons, it is a fact that the Sun has zero moons. Also, the stars have multiple planets revolving around them and in the same way, the Sun also has eight planets revolving around it.
Can you fit 1000 Earths in the Sun?
The answer is that it would take 1.3 million Earths to fill up the Sun. That’s a lot of Earths. The Sun makes up 99.86% of the mass of the Solar System. And it’s the giant planets like Jupiter and Saturn which make the most of that remaining .
How many Jupiter can fit in sun?
According to multiple studies, around 1,000 Jupiters could fit into the Sun. This calculation was done using the volume of the Sun compared to the…
Will the Sun ever burn out?
But in about 5 billion years, the sun will run out of hydrogen. Our star is currently in the most stable phase of its life cycle and has been since the formation of our solar system, about 4.5 billion years ago.
Why haven’t we visited planets in our solar system?
So why haven’t humans yet traveled to Mars? According to NASA, there are a number of obstacles that we still need to overcome before sending a human mission to the planet, including technological innovation and a better understanding of the human body, mind and how we might adapt to life on another planet.
How much longer will the Sun last?
So our Sun is about halfway through its life. But don’t worry. It still has about 5,000,000,000—five billion—years to go. When those five billion years are up, the Sun will become a red giant.
Are there 181 moons in our solar system?
There are 181 known moons in our Solar System which are orbiting planets and dwarf planets. Despite there being so many moons not every planet or dwarf planet has a moon. A table of planets and dwarf planets with the number of moons is below.
Can moons have moons?
Yes, in theory, moons can have moons. The region of space around a satellite where a sub-satellite can exist is called the Hill sphere. Outside the Hill sphere, a sub-satellite would be lost from its orbit about the satellite. An easy example is the Sun-Earth-Moon system.
Does Earth have 2 moons?
The simple answer is that Earth has only one moon, which we call “the moon”. It is the largest and brightest object in the night sky, and the only solar system body besides Earth that humans have visited in our space exploration efforts.
Are there 170 named moons?
Scientists usually refer to them as planetary satellites (human-made satellites are sometimes called artificial moons). There are about 170 moons in our Solar System. Most of them are in orbit around the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn.
Can Suns have moons?
How many people can fit in the Sun?
063 cubic metres (to 3 decimal places). Therefore the amount of people that can fit in the sun’s volume is (1.4 * 10^27)/0.063 which comes out as 2.2 * 10^28 or 22 billion billion billion people.
Can 50 moons fit in the Earth?
The Earth is significantly larger than the moon so around 50 moons would fit in the Earth. The volume of the Earth is 260 billion cubic miles.
Is the Moon 1/4 the size of Earth?
The moon is a bit more than one-quarter (27 percent) the size of Earth, a much larger ratio (1:4) than any other planets and their moons. Earth’s moon is the fifth largest moon in the solar system.
How many Pluto’s can fit in the sun?
Pluto has a diameter of around 2.376 km / 1.476 mi and a radius of around 1 188 km / 738 mi. It’s not quite a massive planet since it has only 0.01 Earth masses or just 1% of our Earth’s mass. Thus it would take more than 200 million Pluto-sized planets to fill the Sun.
How many Earths could fit in Jupiter?
Jupiter is the largest planet in the solar system. Jupiter is so big that all the other planets in the solar system could fit inside it. More than 1,300 Earths would fit inside Jupiter. Jupiter is the fifth planet from the sun.
How Many Earths Can Fit In The Sun? Curious Universe Facts For Kids!
- Article author: kidadl.com
- Reviews from users: 41413
Ratings
- Top rated: 4.7
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about How Many Earths Can Fit In The Sun? Curious Universe Facts For Kids! Updating …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for How Many Earths Can Fit In The Sun? Curious Universe Facts For Kids! Updating While looking at the small, glowing, coin-sized star in the sky, have you ever wondered how many Earths can fit in the Sun? Keep reading to find out.
- Table of Contents:
How many planet Earths can fit in the Sun
How many Earths can fit in the distance from the Earth to the Sun
How many Earths can fit in the diameter of the Sun
How many of Earth’s Moons can fit in the Sun
How Many Earths Can Fit Inside the Sun? | Facts, Amount & Summary
- Article author: nineplanets.org
- Reviews from users: 16686
Ratings
- Top rated: 4.0
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about How Many Earths Can Fit Inside the Sun? | Facts, Amount & Summary Updating …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for How Many Earths Can Fit Inside the Sun? | Facts, Amount & Summary Updating More than one million Earths could fit inside the Sun if it were hollow. Click for even more facts and information.
- Table of Contents:
Mercury Venus and Mars
Jupiter and Saturn
Uranus and Neptune
Pluto
Did you know
The Eight Planets
Eight Planets for Kids
Five Dwarf Planets
The Solar System
The Solar System for Kids
About Nine Planets
Explore
Quick Links
Latest Buyer’s Guides
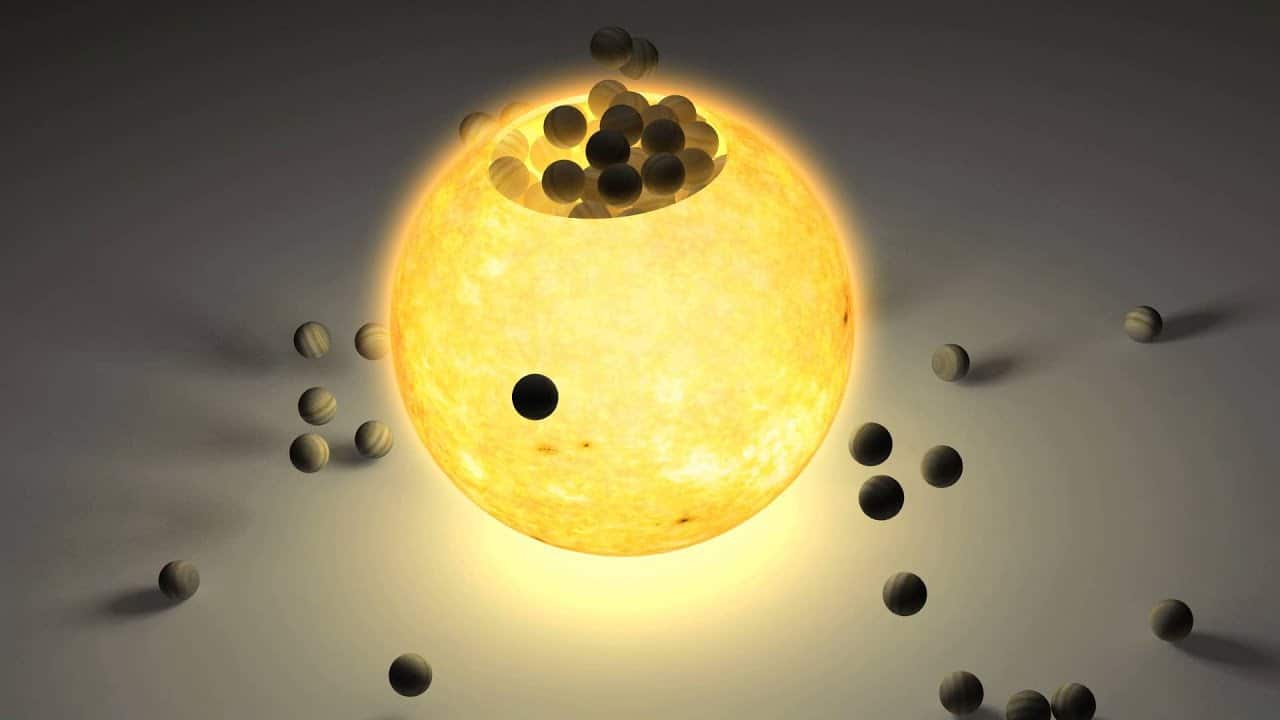
In Depth | Sun – NASA Solar System Exploration
- Article author: solarsystem.nasa.gov
- Reviews from users: 47612
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.4
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about In Depth | Sun – NASA Solar System Exploration Updating …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for In Depth | Sun – NASA Solar System Exploration Updating Planets, Sun, Venus, Earth, Earth’s Moon, Moon, Satellite, Robot, Mars, Asteroid, Jupiter, Europa, Saturn, Enceladus, Titan, Uranus, Neptune, Dwarf Planet, Pluto, Eris, SunNASA’s real-time science encyclopedia of deep space exploration. Our scientists and hardworking robots are exploring the wild frontiers of our solar system.
- Table of Contents:
Namesake
Potential for Life
Size and Distance
Orbit and Rotation
Moons
Rings
Formation
Structure
Surface
Atmosphere
Key Sun Features
Magnetosphere
Resources
Quick Facts
Sun News
More Destinations
Stay Connected
Overview | Moons – NASA Solar System Exploration
- Article author: solarsystem.nasa.gov
- Reviews from users: 33625
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.7
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about Overview | Moons – NASA Solar System Exploration Updating …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for Overview | Moons – NASA Solar System Exploration Updating Planets, Sun, Venus, Earth, Earth’s Moon, Moon, Satellite, Robot, Mars, Asteroid, Jupiter, Europa, Saturn, Enceladus, Titan, Uranus, Neptune, Dwarf Planet, Pluto, Eris, MoonsMoons, also known as natural satellites, orbit planets and asteroids.
- Table of Contents:
What is a Moon
Explore in 3D—Eyes on the Solar System
Moons News
More Destinations
Stay Connected
How many moons does the Sun have class 6 social science CBSE
- Article author: www.vedantu.com
- Reviews from users: 41912
Ratings
- Top rated: 4.4
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about How many moons does the Sun have class 6 social science CBSE Updating …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for How many moons does the Sun have class 6 social science CBSE Updating How many moons does the Sun have
- Table of Contents:

How Many Earths Can Fit Inside the Sun? | Facts, Amount & Summary
- Article author: nineplanets.org
- Reviews from users: 21798
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.4
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about How Many Earths Can Fit Inside the Sun? | Facts, Amount & Summary It would take around 64.3 million Moons to fit inse the Sun, filling it whole. If we were to fill the Earth with Moons, we would need approximately 50 Moons … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for How Many Earths Can Fit Inside the Sun? | Facts, Amount & Summary It would take around 64.3 million Moons to fit inse the Sun, filling it whole. If we were to fill the Earth with Moons, we would need approximately 50 Moons … More than one million Earths could fit inside the Sun if it were hollow. Click for even more facts and information.
- Table of Contents:
Mercury Venus and Mars
Jupiter and Saturn
Uranus and Neptune
Pluto
Did you know
The Eight Planets
Eight Planets for Kids
Five Dwarf Planets
The Solar System
The Solar System for Kids
About Nine Planets
Explore
Quick Links
Latest Buyer’s Guides

How Many Moons Could Fit Inside the Sun
- Article author: shayna-blogolson.blogspot.com
- Reviews from users: 31309
Ratings
- Top rated: 4.0
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about How Many Moons Could Fit Inside the Sun . It would take around 643 million Moons to fit inse the Sun filling it whole. It has a circumference of about 27 million miles. More than one million Earths … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for How Many Moons Could Fit Inside the Sun . It would take around 643 million Moons to fit inse the Sun filling it whole. It has a circumference of about 27 million miles. More than one million Earths …
- Table of Contents:
How many Earths can you fit inside the sun?
- Article author: www.zmescience.com
- Reviews from users: 6548
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.2
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about How many Earths can you fit inside the sun? Volume-wise, you could fit nearly 1.3 million Earths into the sun (1.412 x 1018 km3). That’s assuming all those millions of Earths are squished … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for How many Earths can you fit inside the sun? Volume-wise, you could fit nearly 1.3 million Earths into the sun (1.412 x 1018 km3). That’s assuming all those millions of Earths are squished … You could fit nearly one million Earth-sized planets and the sun isn’t even that big of a star.
- Table of Contents:

How many moons can fit across the sun? – Answers
- Article author: www.answers.com
- Reviews from users: 45805
Ratings
- Top rated: 4.2
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about How many moons can fit across the sun? – Answers Approximately 72 million Earth moons could fit inse the sun. How many Earths would fit across the sun? about one million Earths can fit inse … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for How many moons can fit across the sun? – Answers Approximately 72 million Earth moons could fit inse the sun. How many Earths would fit across the sun? about one million Earths can fit inse … The Sun has about 400 times the diameter of the Moon.The Sun has about 400 times the diameter of the Moon.The Sun has about 400 times the diameter of the Moon.The Sun has about 400 times the diameter of the Moon.
- Table of Contents:
Astronomy
How long does it take for the solar system to make one orbit around the Milky Way galactic center
What layer of the sun moves heat from the radiative layer to the photosphere
Which of these determines the intensity of a volcano
During earthquakes which type of fault results when one plate is compressed up onto another plate
Add your answer
How many moons would fit across the diameter of the sun
Subjects
Top Categories
Company
Product
Legal

how many moons could fit inside the sun
- Article author: study.com
- Reviews from users: 40037
Ratings
- Top rated: 4.7
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about how many moons could fit inside the sun Question: How many moons can fit inse the Sun? Sun: The Sun is the largest object in our solar system. It has a circumference of about 2.7 million miles … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for how many moons could fit inside the sun Question: How many moons can fit inse the Sun? Sun: The Sun is the largest object in our solar system. It has a circumference of about 2.7 million miles …
- Table of Contents:

How Many Moons Could Fit Inside the Sun
- Article author: vicentedesnhjackson.blogspot.com
- Reviews from users: 27583
Ratings
- Top rated: 4.2
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about How Many Moons Could Fit Inside the Sun How Many Moons Can You Fit In The SunIt would take around 643 million Moons to fit inse the Sun filling it whole. It has a circumference of about 27 … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for How Many Moons Could Fit Inside the Sun How Many Moons Can You Fit In The SunIt would take around 643 million Moons to fit inse the Sun filling it whole. It has a circumference of about 27 …
- Table of Contents:
Error 403 (Forbidden)
- Article author: www.quora.com
- Reviews from users: 25151
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.9
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about Error 403 (Forbidden) Earth is about 6371 km big in size, and Moon is about 1734 km (one-fourth of the diameter of Earth) Earth is too big to fit inse of the moon. …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for Error 403 (Forbidden) Earth is about 6371 km big in size, and Moon is about 1734 km (one-fourth of the diameter of Earth) Earth is too big to fit inse of the moon.
- Table of Contents:

See more articles in the same category here: Top 975 tips update new.
How Many Earths Can Fit In The Sun? Curious Universe Facts For Kids!
Our home, the solar system, is studded with a beautiful star, the Sun, and eight diverse planets that orbit around it.
Third among the planets, the Earth is the only known habitable planet in the solar system. Life on Earth has been possible because it is placed at a distance just right from the Sun.
Other planets in the solar system each have a unique characteristic that defines them. Mercury, the planet in the closest proximity to the Sun, is the smallest planet in the solar system. Venus, the brightest visible planet from Earth, is the hottest planet in the solar system. Mars, the fourth planet, is the second most habitable planet for humans owing to its somewhat Earth-like environment. Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system. Saturn has beautiful icy rings around it, and it is also the planet with the most natural satellites. Uranus is unique in the way it rotates at a 90° angle from its orbital plane. Neptune is the farthest of the planets from the Sun and is a bright, vivid blue.
If you find this article informative and fun, also read: how many edges does a cube have and how many nerves are in the human body by Kidadl.
How many planet Earths can fit in the Sun?
The volume of the Sun is approximately 338 x 1015 mi3 (1.40 x 1018 km3), and the volume of Earth is 260 x 109 mi3 (1.08 x 1012 km3) roughly.
If we do the math, a total of 1.3 million Earths can fit inside the Sun. This count is accurate only if we assume these Earths are squished together and leave no space. If we fit perfectly spherical Earths inside the Sun, only 960,000 would be enough to fill the space.
The Sun isn’t only giant; it is very, very heavy too. The Sun’s mass weighs 330,000 times that of the Earth’s. The Sun’s mass is 1,000 times that of even the largest planet in the solar system, Jupiter.
This shows how truly giant our Sun is. It is even more amazing to know that so many stars in the universe are much larger than our Sun. The biggest star to date, UY Scuti, has a volume that is 5 billion times the volume of the Sun, which means 650 x 1013 Earths could fit inside it.
The size of a star changes during its evolutionary process. Most stars become a red giant mass when they exhaust their hydrogen supply and grow massively towards the end of their existence. These red giants are as large as 100 to 1,000 times the size of our Sun. That means a total of 130 million to 1.3 billion Earths could fit inside a red giant. This proves that our vast universe is more spectacular than we can ever comprehend.
How many Earths can fit in the distance from the Earth to the Sun?
The biggest member of the solar system family, our star, the Sun, looks like the size of a big grapefruit to us because of the massive space between our home planet and its parent star.
This distance equates to about 93 million mi (149 million km). In contrast, our beloved Earth stretches across only 7,917 mi (12,742 km) in diameter. This means about 11,745 Earths can fit in the distance between the giant gas ball and our blue planet.
On the other hand, only 107 Suns will be enough to fill this. It just shows how genuinely giant our Sun is.
What’s even more fascinating is that stars much bigger than our Sun exist in our galaxy, and galaxies much bigger than ours are aplenty in our universe.
How many Earths can fit in the diameter of the Sun?
The Sun’s diameter stretches to a whopping 865,370 mi (1,392,678 km), and its radius is 432,685 mi (696,339 km).
So, if Earth-sized planets each with a diameter around 7,900 mi (12,714 km) and a radius around 3,950 mi (6357 km), are placed one next to the other along the Sun’s diameter, 109 planets like our home planet can fit in the Sun’s diameter.
The biggest of planets, Jupiter, whose radius is 43,440 mi (69,910 km), can fill the Sun’s diameter if just 10 of them are placed side by side. On the other hand, Mercury, the smallest planet with a radius of 1,516 mi (2,440 km), can fit nearly 570 of itself along the Sun’s diameter.
How many of Earth’s Moons can fit in the Sun?
The beautiful, white, celestial object filled with craters that keeps waning and filling, decorating our night skies, is the Earth’s natural satellite, the Moon.
In terms of volume, the Moon, measuring up to 5.2 billion mi3 (8.4 billion km3), only equals one-fiftieth of the Earth’s volume. This means the number of Moons required to fill the Sun is 50 times more than the number of Earths required. So, a total of 65 million Moons can fit inside the Sun.
Since our parent star, the Sun, is the largest object in the solar system, all other planets and satellites can fill it up in various numbers. It takes seven million of our neighboring planet, Mars, to fill the Sun, whereas only 1,000 of the largest planet, Jupiter, is sufficient to fill up the Sun. However, the smallest of planets, Mercury, needs 23.2 million of itself to fill the Sun.
Here at Kidadl, we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly facts for everyone to enjoy! If you liked our suggestions for ‘how many Earths can fit in the Sun? Curious universe facts for kids!’ then why not take a look at how do you know when mushrooms are bad or how does a rooster fertilize an egg?
How Many Earths Can Fit Inside the Sun?
Our Sun is the biggest celestial object in the Solar System, containing 99.8% of all the Solar System’s mass. Compared to Earth, which has a mass of around 5.9 quadrillion kg, the Sun is 330.000 times more massive than our little home planet.
Jupiter, the largest planet in our Solar System, has 318 Earth masses, while Mercury, the smallest planet, has only 0.055 Earth Masses. With that being said, how many Earths can fit inside the Sun?
More than one million Earths could fit inside the Sun if it were hollow. The Sun has a radius of 696.340 km / 432.685 mi and a diameter of 1.39 million km / 864.000 mi.
Earth, for comparison, has a radius of only 2.439 km / 1.516 mi, and a diameter of just 12.742 km / 7.917 mi. All the planets in our Solar System combined account for just 0.2% of the Sun’s mass. However, how do the other planets fare in these comparisons? Let’s find out!
Mercury, Venus, and Mars
Mercury is the smallest planet in our Solar System, having a diameter of only 4.879 km / 3.032 mi, and a radius of 2.439 km / 1.516 mi, and only 0.055 Earth masses.
It would take around more than 21.2 million Mercury-sized planets to fit inside the Sun. When it comes to Venus, things get a bit different. Venus is the sixth-largest planet from the Sun, having a diameter of 12.104 km / 7.521 mi, and a radius of around 6.051 km / 3.760 mi. The mass of Venus is equivalent to 0.9 Earth masses, or 90% of our Earth’s mass.
When comparing Venus to the Sun, it starts to shrink drastically, as you could fit 1.5 million Venus-sized planets inside the Sun, if it were hallowed.
Now let’s talk about Mars. Mars is the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, having a diameter of only 6.779 km / 4.212 mi (30% bigger than Mercury), and a radius of 3.389 km / 2.105 mi. Mars has only 11% of our Earth’s mass or 0.11 Earth masses. It would take around 7 million Mars-sized planets to fill the Sun.
Jupiter and Saturn
Moving on to the great gas giants, Jupiter and Saturn, the numbers start to go down or up in other cases. Jupiter is the biggest planet in our Solar System but pales when compared in size to the Sun and any other aspects.
Jupiter has a diameter of around 142.984 km / 88.846 mi at the equator, and a diameter of about 133.708 km / 83.082 mi at the poles. It has a mean radius of 69.911 km / 43.440 mi, and its mass is equivalent to 318 Earth masses. You could fit 1.300 Earths inside Jupiter.
Jupiter might seem impressive in these regards, but it would only take around 1.000 Jupiter-sized planets to fill the Sun. When it comes to Saturn, which is the second-largest planet in our Solar System, things start to change.
Saturn has a diameter of approximately 120.536 km / 74.897 mi and a radius of around 58.232 km / 36.183 mi. It is quite massive as well, having the equivalent of 95.16 Earth masses. It would take more than 1,700 Saturn-sized planets to fill the Sun.
Uranus and Neptune
The icy giants, Uranus and Neptune, are a bit similar in size and mass but lets how they fare against the Sun. Let’s start with Uranus, which is the third-largest planet in the Solar System. Uranus has a diameter of around 51.118 km / 31.763 mi and a radius of 25.362 km / 15.759 mi.
Uranus is reasonably massive, with its mass being equivalent to 14.54 Earth masses. It would take around 22.000 Uranus-sized planets to fill the Sun. Things differ a bit when it comes to Neptune.
Neptune is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System, having a diameter of 49.244 km / 30.598 mi, and a radius of 24.764 km / 15.387 mi. The mass of Neptun is equivalent to 17.15 Earth masses. You can fit around more than 1,800 Neptune-sized planets inside the Sun.
Pluto
Let’s talk about a planet that no longer fits in, yes, the dwarf planet Pluto. Pluto is the ninth-largest planet in the Solar System, and though many don’t regard it as a planet anymore, we figured it deserves a spot here regardless.
Pluto has a diameter of around 2.376 km / 1.476 mi and a radius of around 1,188 km / 738 mi. It’s not quite a massive planet, since it has only 0.01 Earth masses or just 1% of our Earth’s mass. Thus, it would take more than 200 million Pluto-sized planets to fill the Sun.
But if we are going to talk small, let’s talk about our Moon. Earth’s Moon has a diameter of around 3.474 km / 2.158 mi and a radius of 1.737 km / 1.079 mi. In comparison to Earth, the Moon has only 1.2% of Earth’s mass, or in another way of looking at it, the Earth is 81 times heavier than the Moon.
It would take around 64.3 million Moons to fit inside the Sun, filling it whole. If we were to fill the Earth with Moons, we would need approximately 50 Moons to do so.
Did you know?
The largest moon in the Solar System is Ganymede, which is also the most massive moon in our system, and the biggest moon of Jupiter.
Ganymede is larger than the dwarf planet Pluto, or the planet Mercury, or Mars, having a diameter of 5.268 km / 3.273 mi.
The Solar System is quite huge, as you can fit 278.8 billion Sun’s in it. Comparing our Sun to other giant celestial stars , such as the supergiant red star UY Scuti , it would take around 3.69 billion Sun’s to fill UY Scuti. Now imagine comparing the planets of the Solar System to UY Scuti.
Some theorize that if Jupiter were around 70 times or more massive than it currently is, it would have become a star.
Sources:
Image Sources:
Sun – NASA Solar System Exploration
Introduction
The Sun is a 4.5 billion-year-old yellow dwarf star – a hot glowing ball of hydrogen and helium – at the center of our solar system. It’s about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) from Earth and it’s our solar system’s only star. Without the Sun’s energy, life as we know it could not exist on our home planet.
From our vantage point on Earth, the Sun may appear like an unchanging source of light and heat in the sky. But the Sun is a dynamic star, constantly changing and sending energy out into space. The science of studying the Sun and its influence throughout the solar system is called heliophysics.
The Sun is the largest object in our solar system. Its diameter is about 865,000 miles (1.4 million kilometers). Its gravity holds the solar system together, keeping everything from the biggest planets to the smallest bits of debris in orbit around it.
Even though the Sun is the center of our solar system and essential to our survival, it’s only an average star in terms of its size. Stars up to 100 times larger have been found. And many solar systems have more than one star. By studying our Sun, scientists can better understand the workings of distant stars.
The hottest part of the Sun is its core, where temperatures top 27 million °F (15 million °C). The part of the Sun we call its surface – the photosphere – is a relatively cool 10,000 °F (5,500 °C). In one of the Sun’s biggest mysteries, the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona, gets hotter the farther it stretches from the surface. The corona reaches up to 3.5 million °F (2 million °C) – much, much hotter than the photosphere.
Dec. 2, 2020, marked the 25th anniversary of the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO. Since its launch, the mission has kept watch on the Sun.
Namesake
Namesake
The Sun has been called by many names. The Latin word for Sun is “sol,” which is the main adjective for all things Sun-related: solar. Helios, the Sun god in ancient Greek mythology, lends his name to many Sun-related terms as well, such as heliosphere and helioseismology.
Potential for Life
Potential for Life
The Sun could not harbor life as we know it because of its extreme temperatures and radiation. Yet life on Earth is only possible because of the Sun’s light and energy.
Size and Distance
Size and Distance
Our Sun is a medium-sized star with a radius of about 435,000 miles (700,000 kilometers). Many stars are much larger – but the Sun is far more massive than our home planet: it would take more than 330,000 Earths to match the mass of the Sun, and it would take 1.3 million Earths to fill the Sun’s volume.
The Sun is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) from Earth. Its nearest stellar neighbor is the Alpha Centauri triple star system: red dwarf star Proxima Centauri is 4.24 light-years away, and Alpha Centauri A and B – two sunlike stars orbiting each other – are 4.37 light-years away. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year, which equals about 6 trillion miles (9.5 trillion kilometers).
Orbit and Rotation
Orbit and Rotation
The Sun is located in the Milky Way galaxy in a spiral arm called the Orion Spur that extends outward from the Sagittarius arm.
This illustration shows the spiral arms of our Milky Way galaxy. Our Sun is in the Orion Spur. Credit: NASA/Adler/U. Chicago/Wesleyan/JPL-Caltech | Full caption and image
The Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way, bringing with it the planets, asteroids, comets, and other objects in our solar system. Our solar system is moving with an average velocity of 450,000 miles per hour (720,000 kilometers per hour). But even at this speed, it takes about 230 million years for the Sun to make one complete trip around the Milky Way.
The Sun rotates on its axis as it revolves around the galaxy. Its spin has a tilt of 7.25 degrees with respect to the plane of the planets’ orbits. Since the Sun is not solid, different parts rotate at different rates. At the equator, the Sun spins around once about every 25 Earth days, but at its poles, the Sun rotates once on its axis every 36 Earth days.
Moons
As a star, the Sun doesn’t have any moons, but the planets and their moons orbit the Sun.
Rings
Rings
The Sun would have been surrounded by a disk of gas and dust early in its history when the solar system was first forming, about 4.6 billion years ago. Some of that dust is still around today, in several dust rings that circle the Sun. They trace the orbits of planets, whose gravity tugs dust into place around the Sun.
Formation
Formation
The Sun formed about 4.6 billion years ago in a giant, spinning cloud of gas and dust called the solar nebula. As the nebula collapsed under its own gravity, it spun faster and flattened into a disk. Most of the nebula’s material was pulled toward the center to form our Sun, which accounts for 99.8% of our solar system’s mass. Much of the remaining material formed the planets and other objects that now orbit the Sun. (The rest of the leftover gas and dust was blown away by the young Sun’s early solar wind.)
Like all stars, our Sun will eventually run out of energy. When it starts to die, the Sun will expand into a red giant star, becoming so large that it will engulf Mercury and Venus, and possibly Earth as well. Scientists predict the Sun is a little less than halfway through its lifetime and will last another 5 billion years or so before it becomes a white dwarf.
A 3D model of the Sun, our star. Credit: NASA Visualization Technology Applications and Development (VTAD) › Download Options
Structure
Structure
The Sun is a huge ball of hydrogen and helium held together by its own gravity.
The Sun has several regions. The interior regions include the core, the radiative zone, and the convection zone. Moving outward – the visible surface or photosphere is next, then the chromosphere, followed by the transition zone, and then the corona – the Sun’s expansive outer atmosphere.
Once material leaves the corona at supersonic speeds, it becomes the solar wind, which forms a huge magnetic “bubble” around the Sun, called the heliosphere. The heliosphere extends beyond the orbit of the planets in our solar system. Thus, Earth exists inside the Sun’s atmosphere. Outside the heliosphere is interstellar space.
The core is the hottest part of the Sun. Nuclear reactions here – where hydrogen is fused to form helium – power the Sun’s heat and light. Temperatures top 27 million °F (15 million °C) and it’s about 86,000 miles (138,000 kilometers) thick. The density of the Sun’s core is about 150 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). That is approximately 8 times the density of gold (19.3 g/cm³) or 13 times the density of lead (11.3 g/cm³).
Energy from the core is carried outward by radiation. This radiation bounces around the radiative zone, taking about 170,000 years to get from the core to the top of the convection zone. Moving outward, in the convection zone, the temperature drops below 3.5 million °F (2 million °C). Here, large bubbles of hot plasma (a soup of ionized atoms) move upward toward the photosphere, which is the layer we think of as the Sun’s surface.
Surface
Surface
The Sun doesn’t have a solid surface like Earth and the other rocky planets and moons. The part of the Sun commonly called its surface is the photosphere. The word photosphere means “light sphere” – which is apt because this is the layer that emits the most visible light. It’s what we see from Earth with our eyes. (Hopefully, it goes without saying – but never look directly at the Sun without protecting your eyes.)
Although we call it the surface, the photosphere is actually the first layer of the solar atmosphere. It’s about 250 miles thick, with temperatures reaching about 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit (5,500 degrees Celsius). That’s much cooler than the blazing core, but it’s still hot enough to make carbon – like diamonds and graphite – not just melt, but boil. Most of the Sun’s radiation escapes outward from the photosphere into space.
Atmosphere
Atmosphere
Above the photosphere is the chromosphere, the transition zone, and the corona. Not all scientists refer to the transition zone as its own region – it is simply the thin layer where the chromosphere rapidly heats and becomes the corona. The photosphere, chromosphere, and corona are all part of the Sun’s atmosphere. (The corona is sometimes casually referred to as “the Sun’s atmosphere,” but it is actually the Sun’s upper atmosphere.)
The Sun’s atmosphere is where we see features such as sunspots, coronal holes, and solar flares.
Key Sun Features
Visible light from these top regions of the Sun is usually too weak to be seen against the brighter photosphere, but during total solar eclipses, when the Moon covers the photosphere, the chromosphere looks like a fine, red rim around the Sun, while the corona forms a beautiful white crown (“corona” means crown in Latin and Spanish) with plasma streamers narrowing outward, forming shapes that look like flower petals.
In one of the Sun’s biggest mysteries, the corona is much hotter than the layers immediately below it. (Imagine walking away from a bonfire only to get warmer.) The source of coronal heating is a major unsolved puzzle in the study of the Sun.
Magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
The Sun generates magnetic fields that extend out into space to form the interplanetary magnetic field – the magnetic field that pervades our solar system. The field is carried through the solar system by the solar wind – a stream of electrically charged gas blowing outward from the Sun in all directions. The vast bubble of space dominated by the Sun’s magnetic field is called the heliosphere. Since the Sun rotates, the magnetic field spins out into a large rotating spiral, known as the Parker spiral. This spiral has a shape something like the pattern of water from a rotating garden sprinkler.
The Sun doesn’t behave the same way all the time. It goes through phases of high and low activity, which make up the solar cycle. Approximately every 11 years, the Sun’s geographic poles change their magnetic polarity – that is, the north and south magnetic poles swap. During this cycle, the Sun’s photosphere, chromosphere, and corona change from quiet and calm to violently active.
The height of the Sun’s activity cycle, known as solar maximum, is a time of greatly increased solar storm activity. Sunspots, eruptions called solar flares, and coronal mass ejections are common at solar maximum. The latest solar cycle – Solar Cycle 25 – started in December 2019 when solar minimum occurred, according to the Solar Cycle 25 Prediction Panel, an international group of experts co-sponsored by NASA and NOAA. Scientists now expect the Sun’s activity to ramp up toward the next predicted maximum in July 2025.
Solar activity can release huge amounts of energy and particles, some of which impact us here on Earth. Much like weather on Earth, conditions in space – known as space weather – are always changing with the Sun’s activity. “Space weather” can interfere with satellites, GPS, and radio communications. It also can cripple power grids, and corrode pipelines that carry oil and gas.
The strongest geomagnetic storm on record is the Carrington Event, named for British astronomer Richard Carrington who observed the Sept. 1, 1859, solar flare that triggered the event. Telegraph systems worldwide went haywire. Spark discharges shocked telegraph operators and set their telegraph paper on fire. Just before dawn the next day, skies all over Earth erupted in red, green, and purple auroras – the result of energy and particles from the Sun interacting with Earth’s atmosphere. Reportedly, the auroras were so brilliant that newspapers could be read as easily as in daylight. The auroras, or Northern Lights, were visible as far south as Cuba, the Bahamas, Jamaica, El Salvador, and Hawaii.
Another solar flare on March 13, 1989, caused geomagnetic storms that disrupted electric power transmission from the Hydro Québec generating station in Canada, plunging 6 million people into darkness for 9 hours. The 1989 flare also caused power surges that melted power transformers in New Jersey.
In December 2005, X-rays from a solar storm disrupted satellite-to-ground communications and Global Positioning System (GPS) navigation signals for about 10 minutes.
NOAA’s Space Weather Prediction Center monitors active regions on the Sun and issues watches, warnings, and alerts for hazardous space weather events.
Resources
Resources
So you have finished reading the how many moons could fit inside the sun topic article, if you find this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much. See more: All the energy of the earth comes from, Talk about the sun, The birth of the Sun, Fact about the Sun, The biggest star, UY Scuti, Nineplanets org Earth

