You are looking for information, articles, knowledge about the topic nail salons open on sunday near me 랜덤 변수 on Google, you do not find the information you need! Here are the best content compiled and compiled by the https://chewathai27.com/to team, along with other related topics such as: 랜덤 변수 랜덤변수 정의, 확률과 랜덤변수, 확률변수, 랜덤 변수 실험, 랜덤변수의 함수, 랜덤 변수 파이썬, 랜덤변수 종류, 이산랜덤변수
Random variables(랜덤변수) & Distribution function(CDF,누적분포함수) & Density function(PDF,확률밀도함수) : 네이버 블로그
- Article author: m.blog.naver.com
- Reviews from users: 42568
Ratings
- Top rated: 4.6
- Lowest rated: 1
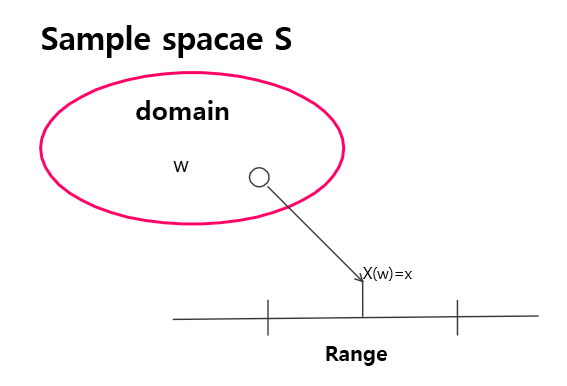
- Summary of article content: Articles about Random variables(랜덤변수) & Distribution function(CDF,누적분포함수) & Density function(PDF,확률밀도함수) : 네이버 블로그 Random variables(랜덤변수, rv)란 event들을 집합이 아닌 조금 더 일반적으로 정의하기 위해 나온 개념으로써, 전체 events들의 집합인 sample sapce S를 … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for Random variables(랜덤변수) & Distribution function(CDF,누적분포함수) & Density function(PDF,확률밀도함수) : 네이버 블로그 Random variables(랜덤변수, rv)란 event들을 집합이 아닌 조금 더 일반적으로 정의하기 위해 나온 개념으로써, 전체 events들의 집합인 sample sapce S를 …
- Table of Contents:
카테고리 이동
공대생을 위한 공부방
이 블로그
확률변수론
카테고리 글
카테고리
이 블로그
확률변수론
카테고리 글
랜덤 변수
- Article author: contents.kocw.or.kr
- Reviews from users: 48924
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.7
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about 랜덤 변수 (예) 이산랜덤변수 X의 누적분포함수가 다음과 같을 때 확률질량함수를 구하라. F. X. x … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for 랜덤 변수 (예) 이산랜덤변수 X의 누적분포함수가 다음과 같을 때 확률질량함수를 구하라. F. X. x …
- Table of Contents:

확률 변수 – 위키백과, 우리 모두의 백과사전
- Article author: ko.wikipedia.org
- Reviews from users: 14024
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.4
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about 확률 변수 – 위키백과, 우리 모두의 백과사전 확률론에서 확률 변수(確率變數, 영어: random variable)는 확률 공간에서 다른 가측 공간으로 가는 가측 함수이다. 시행의 결과에 따라 값이 결정되는 변수를 … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for 확률 변수 – 위키백과, 우리 모두의 백과사전 확률론에서 확률 변수(確率變數, 영어: random variable)는 확률 공간에서 다른 가측 공간으로 가는 가측 함수이다. 시행의 결과에 따라 값이 결정되는 변수를 …
- Table of Contents:
정의[편집]
예[편집]
각주[편집]
참고 문헌[편집]
외부 링크[편집]

RV
- Article author: www.ktword.co.kr
- Reviews from users: 24321
Ratings
- Top rated: 5.0
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about RV Discrete Random Variable, 이산 확률변수, Continuous Random Variable, … Top ▷ 기초과학 ▷ 수학 ▷ 확률/통계 ▷ 확률 과정 ▷ 랜덤과정 용어 … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for RV Discrete Random Variable, 이산 확률변수, Continuous Random Variable, … Top ▷ 기초과학 ▷ 수학 ▷ 확률/통계 ▷ 확률 과정 ▷ 랜덤과정 용어 …
- Table of Contents:

[확률 및 랜덤변수] 2. Random Variables
- Article author: jehunseo.tistory.com
- Reviews from users: 20487
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.3
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about [확률 및 랜덤변수] 2. Random Variables 랜덤 변수 : sample space S의 원소를 실수평면에 연결할 수 있도록 하는 함수. ex. 동전 던지기 – head를 1로, tail을 2로 정의한다. …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for [확률 및 랜덤변수] 2. Random Variables 랜덤 변수 : sample space S의 원소를 실수평면에 연결할 수 있도록 하는 함수. ex. 동전 던지기 – head를 1로, tail을 2로 정의한다. 0. Notation 0. Notation 랜덤변수는 대문자로 표기 ex) W, X, Y, Z, …. 랜덤 변수의 값은 소문자로 표기 ex) w, x, y, z… 1. Definition 랜덤 변수 : sample space S의 원소를 실수평면에 연..Today I Learned…
- Table of Contents:
binomial distribution(이항분포)
Uniform Distribution
Exponential Distribution
Rayleigh Distribution
Conditional Distribution
티스토리툴바
![[확률 및 랜덤변수] 2. Random Variables](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R800x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FwaLmP%2FbtqCPBb2gQj%2FOGkz9nxoJXkufRM6aSwAVK%2Fimg.png)
12. 연속 랜덤 변수 (Continuous Random Variables)
- Article author: skyil.tistory.com
- Reviews from users: 9479
Ratings
- Top rated: 3.7
- Lowest rated: 1
- Summary of article content: Articles about 12. 연속 랜덤 변수 (Continuous Random Variables) 확률 밀도 함수 (Probability Density Function: PDF). 이산 랜덤 변수의 PMF와 같은 함수. fX … …
- Most searched keywords: Whether you are looking for 12. 연속 랜덤 변수 (Continuous Random Variables) 확률 밀도 함수 (Probability Density Function: PDF). 이산 랜덤 변수의 PMF와 같은 함수. fX … 연속 랜덤 변수는 적절한 구간 내의 모든 값을 취하는 랜덤 변수이다. 예를들어, 이 블로그에 5월 20일에 방문한 사람의 수는 이산 랜덤 변수이지만, 이 블로그에서 사람들이 머무른 평균 시간은 연속 랜덤 변수이..
- Table of Contents:
누적 분포 함수 (Cumulative Distribution Function CDF)
확률 밀도 함수 (Probability Density Function PDF)
연속 랜덤 변수의 확률
연속 랜덤 변수의 기댓값 분산 (Expected Value Variance)
연속 랜덤 변수의 성질
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
14 가우시안 랜덤 변수 (Gaussian Random Variable)
13 연속 랜덤 변수의 종류 (Families of Continuous Random Variables)
11 랜덤 변수의 분산과 표준편차 (Variance and Standard Deviation of Random Variable)
10 유도된 랜덤 변수 (Derived Random Variable)
티스토리툴바

See more articles in the same category here: 316+ tips for you.
위키백과, 우리 모두의 백과사전
확률론에서 확률 변수(確率變數, 영어: random variable)는 확률 공간에서 다른 가측 공간으로 가는 가측 함수이다.[1] 시행의 결과에 따라 값이 결정되는 변수를 나타낸다.[2] 가측 함수 조건은 확률 변수가 공역이 되는 가측 공간 위에 새로운 확률 측도를 유도할 수 있도록 하기 위해 필요하다. 이 확률 측도는 흔히 확률 분포라고 부른다.
확률 변수는 아직 실제로 나타나지는 않았지만 나타날 가능성이 있는 모든 경우의 수에 해당하는 값을 가질 수 있다. 주사위를 굴리는 등 실제로 무작위적인 시행에 대해서도 쓸 수 있고, 양자역학처럼 예측 불가능한 물리적 변수의 시행 결과에 대해서도 확률 변수라는 단어를 사용한다. 이처럼 정확히 알지 못하는 어떤 양적 변수의 잠재적인 결과에 대해 확률이라는 단어를 쓸 수 있는가에 대한 논의도 오랜 시간동안 이루어져왔다.
정의 [ 편집 ]
확률 공간 ( Ω , F , Pr ) {\displaystyle (\Omega ,{\mathcal {F}},\Pr )} 위의, 가측 공간 ( E , E ) {\displaystyle (E,{\mathcal {E}})} 의 값을 가지는 확률 변수는 가측 함수 X : ( Ω , F ) → ( E , E ) {\displaystyle X\colon (\Omega ,{\mathcal {F}})\to (E,{\mathcal {E}})} 를 뜻한다. (즉, 임의의 가측 집합 S ∈ E {\displaystyle S\in {\mathcal {E}}} 에 대하여, 사건 X − 1 ( S ) ∈ F {\displaystyle X^{-1}(S)\in {\mathcal {F}}} 및 그 확률을 생각할 수 있다.) 확률론에서는 측도론의 용어를 다음과 같이 대체한다.
확률 변수의 정의역 ( Ω , F , Pr ) {\displaystyle (\Omega ,{\mathcal {F}},\Pr )} 확률 공간 이다.
이다. 확률 변수의 공역 ( E , E ) {\displaystyle (E,{\mathcal {E}})} 상태 공간(狀態空間, 영어: state space )이다.
확률 변수 X : Ω → E {\displaystyle X\colon \Omega \to E} 는 그 상태 공간 E {\displaystyle E} 위에 다음과 같은 확률 측도 Pr ( X ∈ ⋅ ) {\displaystyle \Pr(X\in \cdot )} 를 유도한다.
Pr ( X ∈ S ) = Pr ( X − 1 ( S ) ) ∀ S ∈ E {\displaystyle \Pr(X\in S)=\Pr(X^{-1}(S))\qquad \forall S\in {\mathcal {E}}}
이는 확률 변수 X {\displaystyle X} 가 S {\displaystyle S} 속의 값을 가질 확률이라고 한다. 여기서
X − 1 ( S ) = { ω ∈ Ω : X ( ω ) ∈ S } {\displaystyle X^{-1}(S)=\{\omega \in \Omega \colon X(\omega )\in S\}}
이다.
만약 상태 공간이 위상 공간인 경우, 상태 공간은 통상적으로 보렐 시그마 대수를 사용한다. 예를 들어, 실수 값을 갖는 확률 변수는 실수의 보렐 시그마 대수에 대한 가측 함수이다. (반면, 보렐 시그마 대수 대신 르베그 가측 집합의 시그마 대수를 사용하면, 연속 함수이지만 가측 함수가 아닌 함수들이 존재하게 된다.) 만약 정의역이 이산 확률 공간(즉, 모든 부분 집합이 사건인 확률 공간)일 경우, 모든 함수 Ω → E {\displaystyle \Omega \to E} 는 가측 함수이며, 따라서 정의에서 가측성 조건을 생략할 수 있다.
예 [ 편집 ]
예1 [ 편집 ]
주사위를 던져 나오는 눈의 수를 추상화한 확률 공간
( Ω , F , Pr ) {\displaystyle (\Omega ,{\mathcal {F}},\operatorname {Pr} )} Ω = { 1 , 2 , … , 6 } {\displaystyle \Omega =\{1,2,\dots ,6\}} F = P ( { 1 , 2 , … , 6 } ) {\displaystyle {\mathcal {F}}={\mathcal {P}}(\{1,2,\dots ,6\})} Pr ( { 1 } ) = Pr ( { 2 } ) = Pr ( { 3 } ) = Pr ( { 4 } ) = Pr ( { 5 } ) = Pr ( { 6 } ) = 1 / 6 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (\{1\})=\operatorname {Pr} (\{2\})=\operatorname {Pr} (\{3\})=\operatorname {Pr} (\{4\})=\operatorname {Pr} (\{5\})=\operatorname {Pr} (\{6\})=1/6}
을 생각하자. 즉, 1부터 6까지의 수가 나올 수 있으며, 각각의 수가 나올 확률은 같다. 이 확률 공간 위에 다음과 같은 확률 변수를 정의하자.
X : 2 , 4 , 6 ↦ 0 {\displaystyle X\colon 2,4,6\mapsto 0} X : 1 , 3 , 5 ↦ 1 {\displaystyle X\colon 1,3,5\mapsto 1}
즉, X {\displaystyle X} 는 짝수가 나왔을 경우 0, 홀수가 나왔을 경우 1을 취한다. 그렇다면 주사위를 던져 짝수가 나올 확률은 다음과 같다.
Pr ( X = 0 ) = Pr ( { 2 , 4 , 6 } ) = 1 / 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (X=0)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{2,4,6\})=1/2}
마찬가지로, 홀수가 나올 확률은 다음과 같다.
Pr ( X = 1 ) = Pr ( { 1 , 3 , 5 } ) = 1 / 2 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (X=1)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{1,3,5\})=1/2}
예2 [ 편집 ]
두 개의 주사위를 던진 결과의 확률 공간
( Ω × Ω , F × F , Pr × Pr ) {\displaystyle (\Omega \times \Omega ,{\mathcal {F}}\times {\mathcal {F}},\operatorname {Pr} \times \operatorname {Pr} )}
을 생각하자. 즉, 두 주사위의 눈의 수는 서로 독립이다. 두 눈의 수의 합을 나타내는 확률 변수
Y : ( i , j ) ↦ i + j {\displaystyle Y\colon (i,j)\mapsto i+j}
의 확률 분포는 다음과 같다.
Pr ( Y = 2 ) = Pr ( { ( 1 , 1 ) } ) = 1 / 36 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=2)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(1,1)\})=1/36} Pr ( Y = 3 ) = Pr ( { ( 1 , 2 ) , ( 2 , 1 ) } ) = 1 / 18 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=3)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(1,2),(2,1)\})=1/18} Pr ( Y = 4 ) = Pr ( { ( 1 , 3 ) , ( 2 , 2 ) , ( 3 , 1 ) } ) = 1 / 12 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=4)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(1,3),(2,2),(3,1)\})=1/12} Pr ( Y = 5 ) = Pr ( { ( 1 , 4 ) , ( 2 , 3 ) , ( 3 , 2 ) , ( 4 , 1 ) } ) = 1 / 9 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=5)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(1,4),(2,3),(3,2),(4,1)\})=1/9} Pr ( Y = 6 ) = Pr ( { ( 1 , 5 ) , ( 2 , 4 ) , ( 3 , 3 ) , ( 4 , 2 ) , ( 5 , 1 ) } ) = 5 / 36 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=6)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(1,5),(2,4),(3,3),(4,2),(5,1)\})=5/36} Pr ( Y = 7 ) = Pr ( { ( 1 , 6 ) , ( 2 , 5 ) , ( 3 , 4 ) , ( 4 , 3 ) , ( 5 , 2 ) , ( 6 , 1 ) } ) = 1 / 6 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=7)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(1,6),(2,5),(3,4),(4,3),(5,2),(6,1)\})=1/6} Pr ( Y = 8 ) = Pr ( { ( 2 , 6 ) , ( 3 , 5 ) , ( 4 , 4 ) , ( 5 , 3 ) , ( 6 , 2 ) } ) = 5 / 36 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=8)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(2,6),(3,5),(4,4),(5,3),(6,2)\})=5/36} Pr ( Y = 9 ) = Pr ( { ( 3 , 6 ) , ( 4 , 5 ) , ( 5 , 4 ) , ( 6 , 3 ) } ) = 1 / 9 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=9)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(3,6),(4,5),(5,4),(6,3)\})=1/9} Pr ( Y = 10 ) = Pr ( { ( 4 , 6 ) , ( 5 , 5 ) , ( 6 , 4 ) } ) = 1 / 12 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=10)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(4,6),(5,5),(6,4)\})=1/12} Pr ( Y = 11 ) = Pr ( { ( 5 , 6 ) , ( 6 , 5 ) } ) = 1 / 18 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=11)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(5,6),(6,5)\})=1/18} Pr ( Y = 12 ) = Pr ( { ( 6 , 6 ) } ) = 1 / 36 {\displaystyle \operatorname {Pr} (Y=12)=\operatorname {Pr} (\{(6,6)\})=1/36}
각주 [ 편집 ]
참고 문헌 [ 편집 ]
Doob, Joseph L. (1996년 8월). “The development of rigor in mathematical probability (1900–1950)”. 《The American Mathematical Monthly》 (영어) 103 (7). doi:10.2307/2974673. ISSN 0002-9890. JSTOR 2974673. MR 1404084. Zbl 0865.01011.
Kersting, Götz; Wakolbinger, Anton (2014). 《Zufallsvariable und Stochastische Prozesse》 (독일어). Birkhäuser. ISBN 978-3-7643-8432-6 .
Fahrmeir, Ludwig; Künstler, Rita; Pigeot, Iris; Tutz, Gerhard (2012). 《Statistik: Der Weg zur Datenanalyse》 (독일어) Auflage 7판. Springer. ISBN 978-3-6420-1938-8 .
Papula, Lothar (2011). 《Mathematik für Ingenieure und Naturwissenschaftler Band 3》 (독일어) Auflage 6판. Vieweg+Teubner Verlag. ISBN 978-3-8348-1227-8 .
12. 연속 랜덤 변수 (Continuous Random Variables)
연속 랜덤 변수는 적절한 구간 내의 모든 값을 취하는 랜덤 변수이다.
예를들어, 이 블로그에 5월 20일에 방문한 사람의 수는 이산 랜덤 변수이지만, 이 블로그에서 사람들이 머무른 평균 시간은 연속 랜덤 변수이다.
사람 수는 셀 수 있지만, 시간은 정확히 잴 수 없는 연속된 값이기 때문이다.
누적 분포 함수 (Cumulative Distribution Function: CDF)
임의의 값 $x$까지 랜덤 변수 $X$가 갖는 값.
$$ F_X(x) = P[X \leq x] $$
연속 랜덤 변수의 CDF는 PDF를 적분하여 구할 수 있다.
$$ F_X(x) = \int_{-\infty }^{x} f_X(u)du $$
확률 밀도 함수 (Probability Density Function: PDF)
이산 랜덤 변수의 PMF와 같은 함수.
$$ f_X(x) = \frac{dF_X(x)}{dx} $$
연속 랜덤 변수의 확률
연속 랜덤 변수에서 한 값의 확률은 한 값을 정확히 측정하기 어렵기 때문에 별 의미가 없고, 특정 구간의 확률을 구하여 사용한다.
(컵에 담긴 물이 정확히 100ml일 확률은 0에 수렴하고, 99ml ~ 101ml 사이일 확률을 구한다.)
$$ P[x_1 < X \leq x_2] = \int_{x_1}^{x_2} f_X(x)dx $$ 연속 랜덤 변수의 기댓값, 분산 (Expected Value, Variance) 연속 랜덤 변수의 기댓값은 아래와 같다. $$ E[X] = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} xf_X(x)dx $$ 연속 랜덤 변수의 분산은 이산 랜덤 변수와 다르지 않다. $$ E[(x-\mu x)^2] = E[x^2] - (E[x])^2 $$ 연속 랜덤 변수의 성질 $$ E[X - \mu x] = 0 \\ E[aX+b] = aE[X] + b\\ Var[X] = E[X^2] - \mu ^2x \\ Var[aX+b] = a^2Var[X] $$
So you have finished reading the 랜덤 변수 topic article, if you find this article useful, please share it. Thank you very much. See more: 랜덤변수 정의, 확률과 랜덤변수, 확률변수, 랜덤 변수 실험, 랜덤변수의 함수, 랜덤 변수 파이썬, 랜덤변수 종류, 이산랜덤변수

